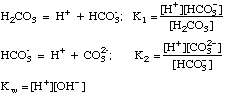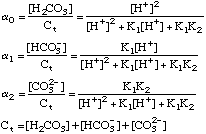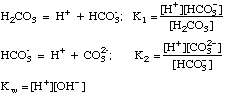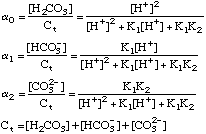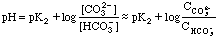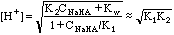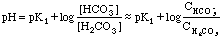Polyprotic Equations Slide
Polyprotic Acid-Base Equations
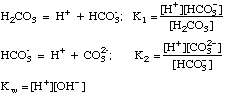
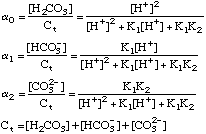
After plugging these terms into a proper charge balance equation we
can produce an advanced solution to any acid-base problem.
For quick and dirty pH calculations for most points in the
polyprotic titration curve, we can divide the curve into the following
regions:
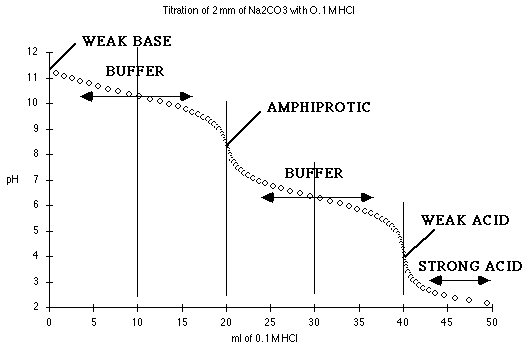
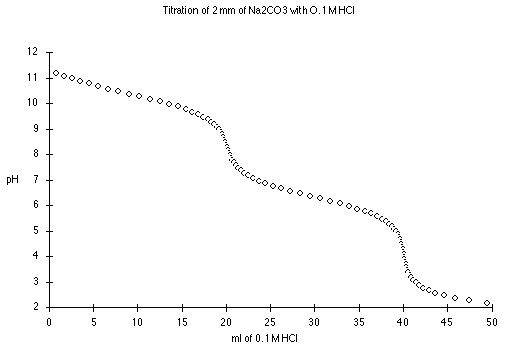
At 0 mL HCl added, we have a solution of pure
Na2CO3. Try treating this as a monoprotic weak base,
where Kb = Kw/K2
Between 5 mL and 15 mL we are in one of the buffer regions. Here
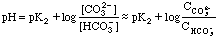
At 20 mL HCl, we have the first end point, and a solution of pure
NaHCO3 in water, an amphiprotic substance.
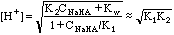
From 25 to 35 mL we have the other buffer region. Here
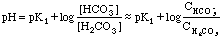
At 40 mL HCl added, we have the equivalent of pure
H2CO3. Try treating this as a monoprotic weak acid
where Ka = K1.
David L. Zellmer, Department of Chemistry, California State University, Fresno. March 17, 1997