

Looked at organizational structure and "dynamics related to bureaucracy"-originator of term BUREAUCRACY
|
|
1. Rules and policies to guide organizational workers-
2. Division of labor:
3. Hierarchy of authority: Chain
of command principle-
decisions appealable to next higher level
4. Expertise: Workers hired for their qualifications Training given
to workers, Hiring and promotion based on merit alone.
Can you think of disadvantages?
Are government officials always selected based on merit or ability?
At what levels should merit or ability become less important?
5. Written rules/orders: Decisions, orders and rules are all recorded in writing.
this is also costly for clients/recipients
of government services:
![]()
The government bureaucracy is costing businesses 46
Billion Euros per year. This cost is the result of the paperwork and application
process with the government. Costs for dealing with the government have increased
by 50% since 1994.
Bureaucratic rules can also inhibit the
provision of services it is designed to deliver:
Firefighting
gear stockpile unused
New Orleans paper rips federal response
6.Lifetime employment: Work/job viewed as career for life. Permanence in position brings stability to organization
TODAY MOST CRIMINAL JUSTICE AGENCIES
ARE BUREAUCRACIES
LEVEL OF BUREAUCRACY DEPENDENT ON:
![]() Size of agency
Size of agency
![]() Organizational hierarchy
Organizational hierarchy
![]() Nature of Organization
Nature of Organization
CRIMINAL JUSTICE ORGANIZATIONS:
POLICE-Difficult to measure input vs. output-no profit/loss
statement
Inability to achieve success by any measure-results in request for increased
funding to do better-though success is not totally dependent on police agency
activities.
PRIVATE SECTOR-Inability to make profit results in bankcruptcy and end of business. Existence generally contingent upon continued profitability.
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE and PRINCIPLES IN TEXT:
 |
What is management? |
 |
What is Leadership? |
- Getting things done through subordinates
- Enforcing policies & procedures-rule by book
- Follows existing practices-rules/plays it safe
- Mechanistic in nature
Leadership
- Making people enthusiastic about their job
- Risk taking
- Breaking rules and creating new ones
- LAO-TZU- (640 B.C.)Leader is a catalyst
Machiavelli studied leaders throughout past
history to determine which leaders were
successful (stayed in power) and why.
Machiavelli on Leadership

1469-1527
| Leaders rule through Love and Fear | |
|
Fear preferable to Love if
using only one method |
|
| The most difficult task for leaders:Discipline someone they care for | |
| Leaders need not necessarily be moral to be successful | |
| Great leadership usually comes about during crisis or during formation of a new state. | |
| Treaties are broken if they no longer serve a useful purpose | |
| Surround yourself with loyal & knowledgeable people |
"How to" primers on Leadership>ephemeral existence
Can you identify a leader who conforms to Machiavelli's description?
TRAIT THEORY
Based on study of 468 administrators in
13 companies researchers
concluded that successful leaders showed the following traits:
Inability to measure above-led to demise of theory.
Can you identify a NON-LEADER "type" who attended or completed leadership training and as a result became a great leader?
STYLE THEORY
Three principles of leadership
behavior
QUESTION: Is every person in a leadership role necessarily a leader?
Why or why not?
Textbook comments:
INSTRUCT0R'S COMMENTS BASED ON RESEARCH & EXPERIENCE:
THEORIES OF MOTIVATION
MOTIVATIONAL THEORY AND PRACTICE
Biggest problem in organizations found by SCHWEIZER:
BARRIERS TO EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION:
PROBLEM: The grapevine (rumors) Real reactions to incorrect unverified information
F.W.TAYLOR
Father
of Scientific Management

1856-1915
Scientific Management Theory
READ ABOUT LEADERSHIP IN TODAYS MILITARY AND CIVILIAN WORLD
MANAGEMENT LITERATURE: Largest theft in industry is theft of TIME by employees.

HUMAN RELATIONS MANAGEMENT
Elton Mayo

1880-1949
Motivation Theory Elton Mayo's Hawthorne Experiments
The Hawthorne Studies
MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
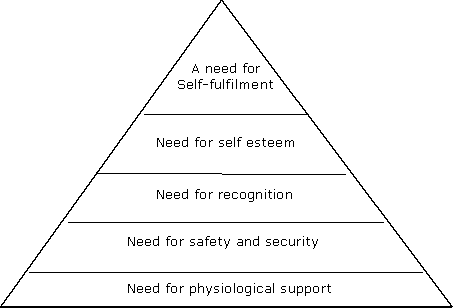
As a chief of police or warden, how would you address each of the above needs among your subordinates?
HERZBERG’S MOTIVATION HYGIENE
Douglas McGregor

1906-1964
McGREGOR'S THEORY X AND Y
Theory X managers-assumptions about average worker
Above View held by many managers
Theory Y managers-assumptions about average worker

Argyris'
Immaturity/Maturity Model
Worker responses to barriers to growth:
INSTRUCTOR:
It is difficult to refute that a worker's maturity
level
has a bearing on motivation and performance. Since
we all operate at different maturity levels, managers
must address these differences in their management
decisions.
American Society for Training
and Development
|
|
Important Concepts/Information:
![]() Each of the three components of the CJ system affect each other.
Each of the three components of the CJ system affect each other.
![]() Agencies within a component, i.e. courts, police or corrections, affect each
other.
Agencies within a component, i.e. courts, police or corrections, affect each
other.
![]() It is important to study all three components since they all affect each other
It is important to study all three components since they all affect each other
![]() It is important to study all three components since all can experience similar
problems.
It is important to study all three components since all can experience similar
problems.
![]() Individual goals and objectives of in
each component may conflict with those of other components.
Individual goals and objectives of in
each component may conflict with those of other components.
![]() There can be no mission for the entire C.J. system since no one is in charge
of it.
There can be no mission for the entire C.J. system since no one is in charge
of it.
![]() Policing in the United States is highly fragmented with more than separate 18,000
agencies
Policing in the United States is highly fragmented with more than separate 18,000
agencies
![]() The goals of one C.J. component may conflict with those of another
The goals of one C.J. component may conflict with those of another
![]() Uniformity among all law enforcement agencies, corrections, and the courts is
not possible
Uniformity among all law enforcement agencies, corrections, and the courts is
not possible
![]() Funding sources differ for most agencies, hence differences in operation, effectiveness,
goals, etc.
Funding sources differ for most agencies, hence differences in operation, effectiveness,
goals, etc.
![]() Some Public Sector jobs can have benefits and rewards similar to private sector
jobs
Some Public Sector jobs can have benefits and rewards similar to private sector
jobs
![]() Some Public Sector jobs simply are not intrinsically rewarding
Some Public Sector jobs simply are not intrinsically rewarding
![]() Our C.J. System is not much of a system
Our C.J. System is not much of a system
![]() There are six crucial elements to a bureaucracy, according to Max Weber
There are six crucial elements to a bureaucracy, according to Max Weber
![]() A bureaucratic structure provides stability and continuity
even as leaders change
A bureaucratic structure provides stability and continuity
even as leaders change
![]() Rules in a bureaucracy can conflict with common sense and impede effectiveness
Rules in a bureaucracy can conflict with common sense and impede effectiveness
![]() The level of bureaucracy may differ depending on the type and nature of an organization
The level of bureaucracy may differ depending on the type and nature of an organization
![]() Management is following and applying rules
Management is following and applying rules
![]() Leadership is breaking them and making new ones
Leadership is breaking them and making new ones
![]() Leaders may become ineffective if they have a strong need to be liked
Leaders may become ineffective if they have a strong need to be liked
![]() Leaders have great difficult disciplining those they care for
Leaders have great difficult disciplining those they care for
![]() Rule based on fear is more stable/better than rule based on love of the leader
Rule based on fear is more stable/better than rule based on love of the leader
![]() Scientific Management Theory used science/math to assess what a worker should
do and how
Scientific Management Theory used science/math to assess what a worker should
do and how
![]() Under S.M.T. all workers are naturally lazy
Under S.M.T. all workers are naturally lazy
![]() Under S.M.T. workers can be motivated by money
Under S.M.T. workers can be motivated by money
![]() Under S.M.T. Management should only involve itself in routine decision making
Under S.M.T. Management should only involve itself in routine decision making
![]() Under S.M.T. it is not possible to determine how much someone can really work.
Under S.M.T. it is not possible to determine how much someone can really work.
![]() Under Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, workers can be motivated by satisfying those
needs
Under Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, workers can be motivated by satisfying those
needs
![]() It is not possible to satisfy all five needs in every organization
It is not possible to satisfy all five needs in every organization
![]() Managers make different assumptions about their workers, which affects their
leadership style
Managers make different assumptions about their workers, which affects their
leadership style
![]() Most managers believe their workers do not like to work and must be coerced
or threatend to do their job
Most managers believe their workers do not like to work and must be coerced
or threatend to do their job
![]() Under the Immaturity/Maturity Model of Chris Argyris, unproductive workers are
not lazy, but immature.
Under the Immaturity/Maturity Model of Chris Argyris, unproductive workers are
not lazy, but immature.
![]() An organization can make workers more or less mature.
An organization can make workers more or less mature.